Food is fuel for your body. Just like a car needs gas to run, your body needs specific nutrients to function. These nutrients are found in the foods you eat. There are six nutrients your body must have to function optimally.
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats
- Water
- Vitamins
- Minerals
You need large amounts of carbs, proteins, fats, and water, and you need small amounts of vitamins and minerals.
The calories in carbs, proteins, and fats provide the body with the energy you need to do things like move, breathe, eat, and think.
Water, vitamins, and minerals do not contain calories, which means your body can’t turn them into energy. However, you need water, vitamins, and minerals to get energy from carbs, proteins, and fats. Not only are water, vitamins, and minerals needed to make energy, they play an important role in many other body processes.
Here is a brief overview of each of the six essential nutrients. These are called essential nutrients because they must be obtained from your diet. Your body cannot produce them on its own in sufficient amounts.
Note: Because I am trying to un-muddy the waters, I have only included the information that I feel is most important when it comes to gaining a basic understanding of food and nutrition.
Carbohydrates

What are carbohydrates?
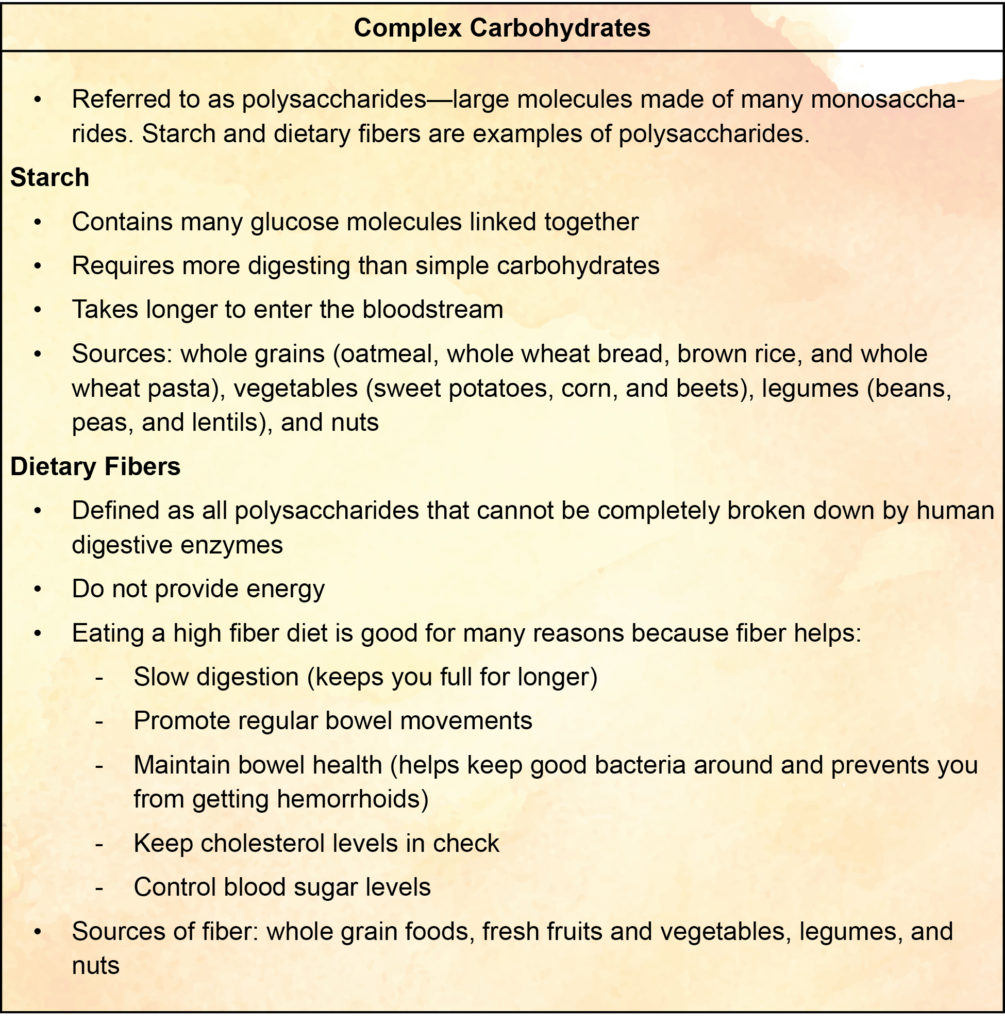
- Sugars, starches, and fibers found in fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy
- There are two categories of carbohydrates: simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates

What do carbohydrates do?
- Provide the body with energy (body’s main energy source)
Proteins
What are proteins?
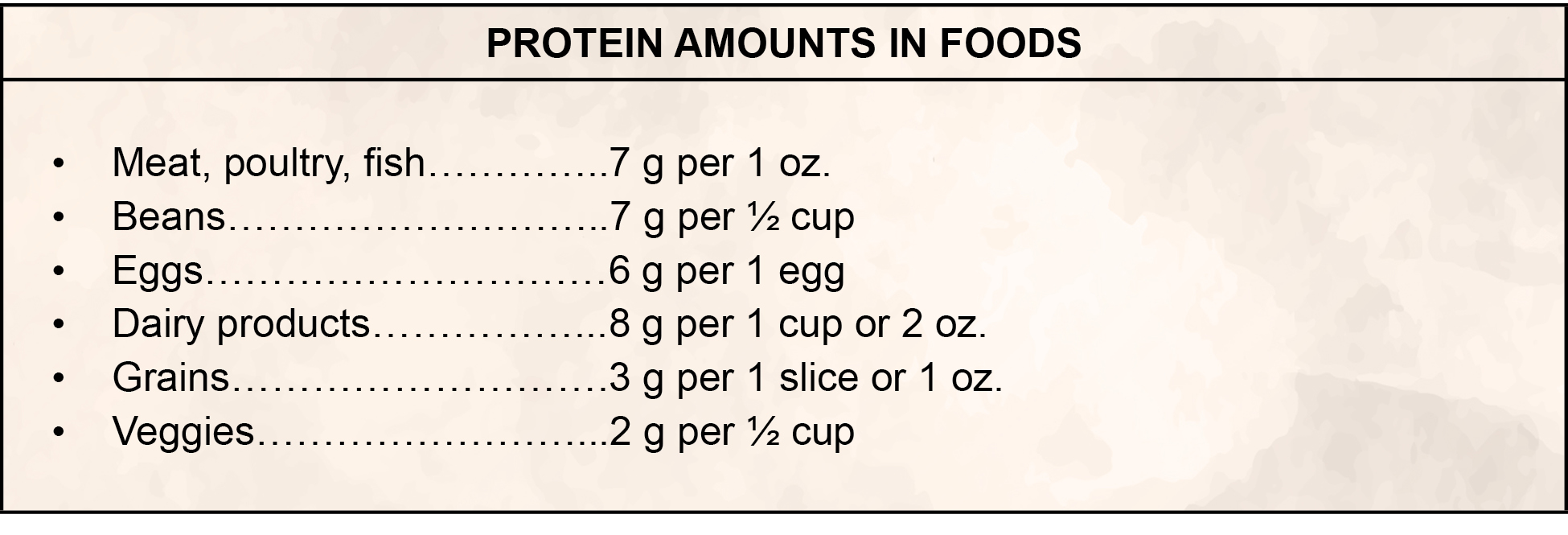
- Groups of amino acids found in meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, dairy, soy products, beans, nuts, and seeds
- Both animal and plant proteins are made up of about 20 amino acids. Each protein contains varying proportions of each, but all food proteins contain some amount of each amino
- There are three categories of amino acids: essential amino acids, non-essential amino acids, and conditional amino

What do proteins do?
- Build, maintain, and repair body tissues (the main building block for muscles)
- Provide a small amount of energy, but only when the body is not getting enough calories from the fat stored in the body or from other nutrients (carbs or fats)
- Proteins take longer to digest which helps you feel full for a longer period

Fats
What are fats?
- Fatty acids found in meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, dairy, plant oils, avocados, nuts, and seeds
- There are three categories of fat: unsaturated fat, saturated fat, and trans fat.
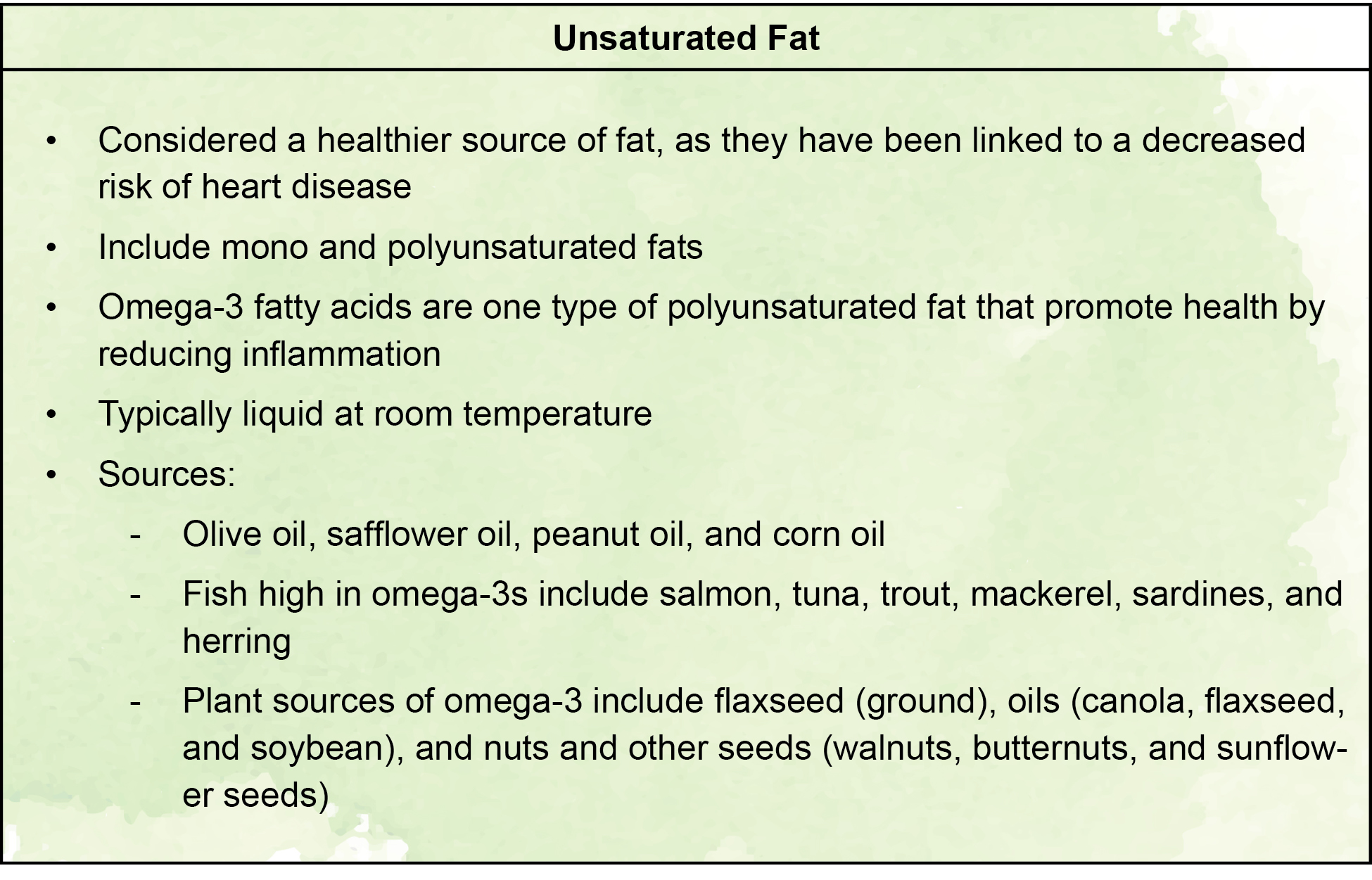

What do fats do?
- Provide the body with energy (typically used at rest and during lower-intensity exercise)
- Fats take longer to digest which helps you stay full for a longer period of time
- Help transport fat-soluble vitamins
- Maintain body temperature (fat tissue = insulation)
- Protect vital organs
Water
What is water?
- Water is a substance composed of two elements: hydrogen and oxygen
- Our bodies are made up of ~60% water
- Best source is drinking water
- Other sources: food (soup, fruits, and veggies) and other beverages (milk, tea, coffee, soda, and juice)
What does water do?
- All cells and organs need water to function (we can’t live without it)
- Specific functions:
- Transports nutrients and oxygen to cells
- Removes toxins from the body
- Protects organs and tissues
- Regulates body temperature
- Lubricates joints
Vitamins

What are vitamins?
- Naturally occurring compounds found in food
- There are two categories of vitamins: water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins.


What do vitamins do?
- Needed for normal growth and development
- Specific functions:
- Promote healthy teeth and gums
- Assist in the absorption of iron and production of red blood cells
- Help the body turn carbs, proteins, and fats into energy
- Maintain skin and nerve health
Minerals

What are minerals?
- Just like vitamins, minerals are naturally occurring compounds found in food
- There are two categories of minerals: macro minerals and trace minerals

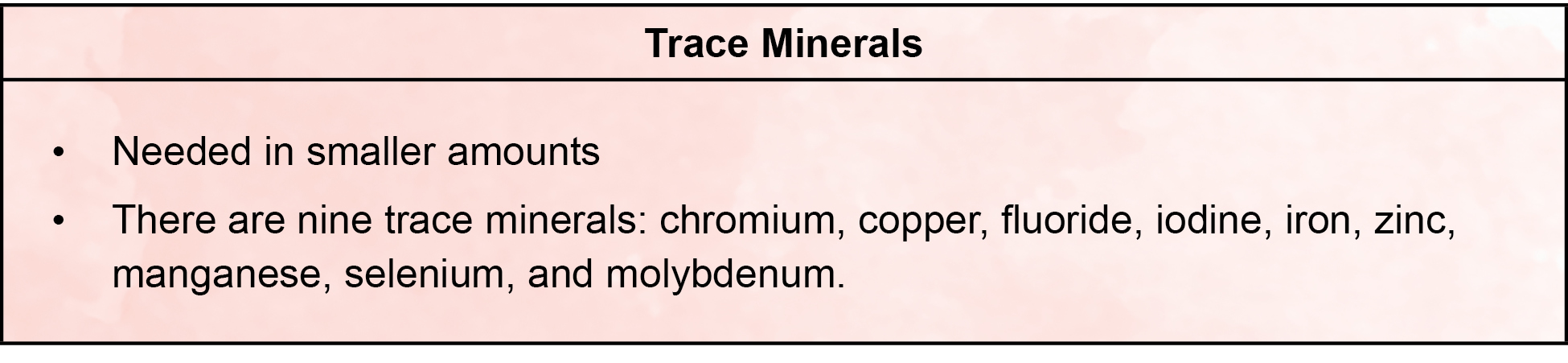
What do minerals do?
- Needed for normal growth and development
- Specific functions:
- Promote nerve and muscle function
- Support tooth and bone formation
- Generate energy from carbs, proteins, and fats
- Maintain thyroid health
- Act as antioxidants
- Regulate fluid balance

Energy Balance
Now that you know a little bit about the specific nutrients that give your body energy in some way, shape, or form, let’s talk about energy balance.
Your body requires a certain amount of energy to carry out its everyday functions. As mentioned previously, you supply your body with energy by eating food. The body then uses this energy to:
- Carry out vital body functions while at rest (like breathing and pumping blood through your body)
- Process food (digest, absorb, transport, turn into energy, and store the foods you eat)
- Maintain body temperature
- Move (walk, run, jump, lift weights, )
Energy balance is achieved when your energy intake equals your energy expenditure.
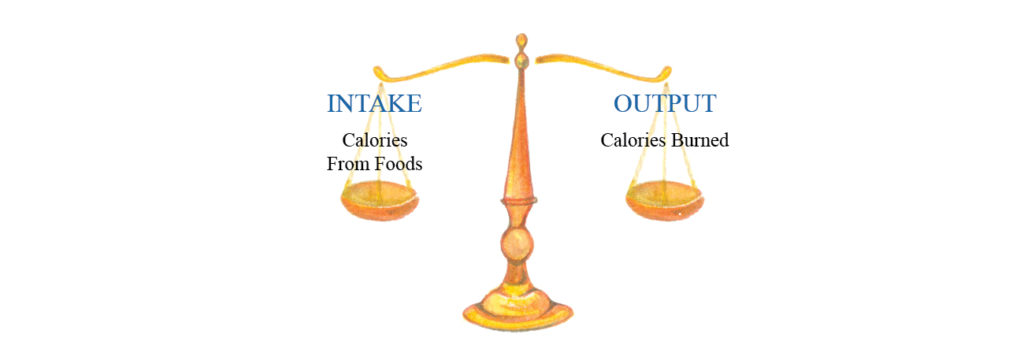
To maintain body weight, you must balance the energy you get from food with the energy you use to carry out body functions, process food, maintain body temperature, and move.
Note: The energy needed to carry out vital body functions, process food, and maintain body temperature stays pretty consistent on a daily basis. Movement (like physical activity) is the most variable factor that can drastically change your energy needs from day-to-day. Moving more increases your energy needs. Moving less decreases your energy needs.
Positive energy balance = weight gain
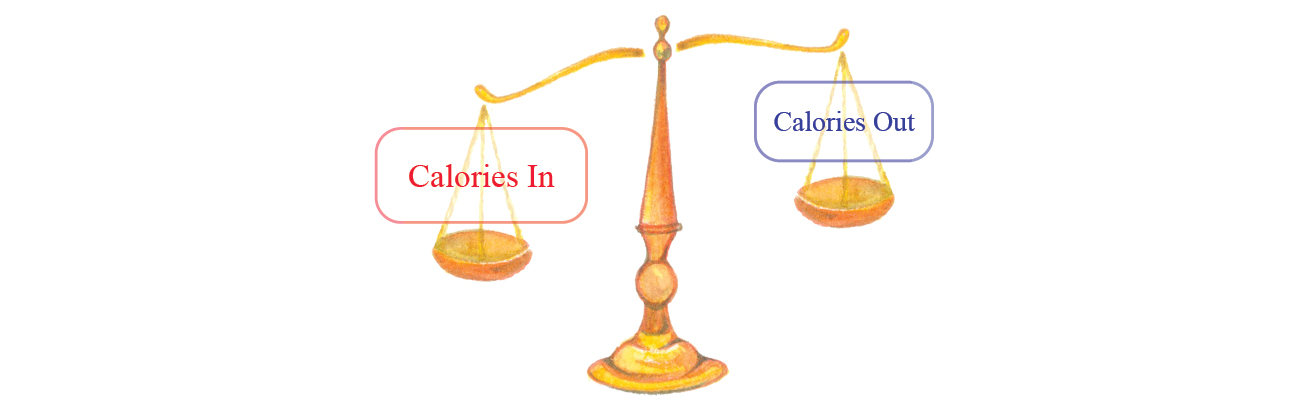
You are said to have a positive energy balance when your energy intake is greater than your energy expenditure.
This means you are taking in more food (energy) than your body is using. In this case, the excess energy is stored as fat and your body weight increases.
Note: A positive energy balance is required to increase muscle mass. In this case, the extra food (energy) you are taking in is used to support the growth of new muscle tissue instead of being stored as fat. But keep in mind that extra food will not necessarily help you gain more muscle. You also need to stress your muscles by adding some form of strength training to your exercise regimen.
Negative energy balance = weight loss
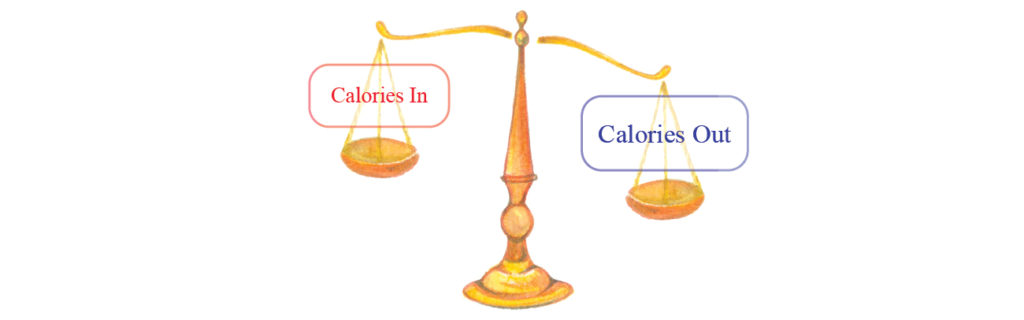
A negative energy balance occurs when your energy intake is less than your energy expenditure.
In other words, you are not taking in enough food (energy) to keep up with the amount of energy the body is using each day. Often, this is the result of a large increase in physical activity with little or no change in food intake. In this case, energy is taken from energy stores in the body and body weight decreases.
If you are looking to lose weight, putting yourself in a negative energy balance is beneficial. This means you are not taking in enough energy to support the body’s needs through food alone and thus, your body has to pull energy from fat stores. This is how you get rid of excess fat.
A word of advice: Starving yourself (eating next to nothing) is not the best way to lose weight.
Why?
Starving yourself will lead to an equal loss of fat and muscle. If you are looking to ditch the fat and keep the muscle, I suggest two things:
1. Eat less
- Decrease your food intake slightly (Small changes will make this process less miserable and will also allow you to get enough nutrients so your body doesn’t start breaking down your muscles for energy.)
- Focus on eating foods that are rich in nutrients and void of empty calories (more fruits and veggies, less cookies and candy)
2. Move more
- Increase your physical activity slightly and do something that you enjoy (Again, the less miserable you are, the more likely you are to stick with it.)
- Add some weight (If you want to build more muscle, you must put stress on the muscles you have. Your body weight might be enough at first, but over time, you will need to add more weight. If this is new to you, hire a personal trainer, join a group fitness class, or download a fitness app to help get you )

Nutrition Recommendations for Healthy Living
Eating for healthy living includes:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Proteins (mostly from whole, plant sources)
- Fats (mostly from whole, plant sources)
- Use oil sparingly as it’s a concentrated source of calories that isn’t very nutrient dense. Buy cold-pressed unrefined oils when possible as they’re extracted without heat or chemicals, which helps preserve the nutrients, vitamins, and antioxidants.
Eating for healthy living limits:
- Saturated and trans fats
- Added sugars
- Sodium
- Alcohol
For all food groups, eat a variety of food choices to make sure you are getting all the nutrients your body needs to stay healthy.
This concludes Step 1: Gain Core Knowledge. You have now acquired the basic nutrition knowledge that is essential for building healthy eating habits. Next up, Step 2: Master the Basics (click the link and scroll down to the section titled Step 2: Master the Basics).